What influences behaviour?
Human behaviour is a complex phenomenon influenced by a myriad of factors. However, renowned social psychologist Kurt Lewin introduced an equation that elegantly captures the essence of this intricate
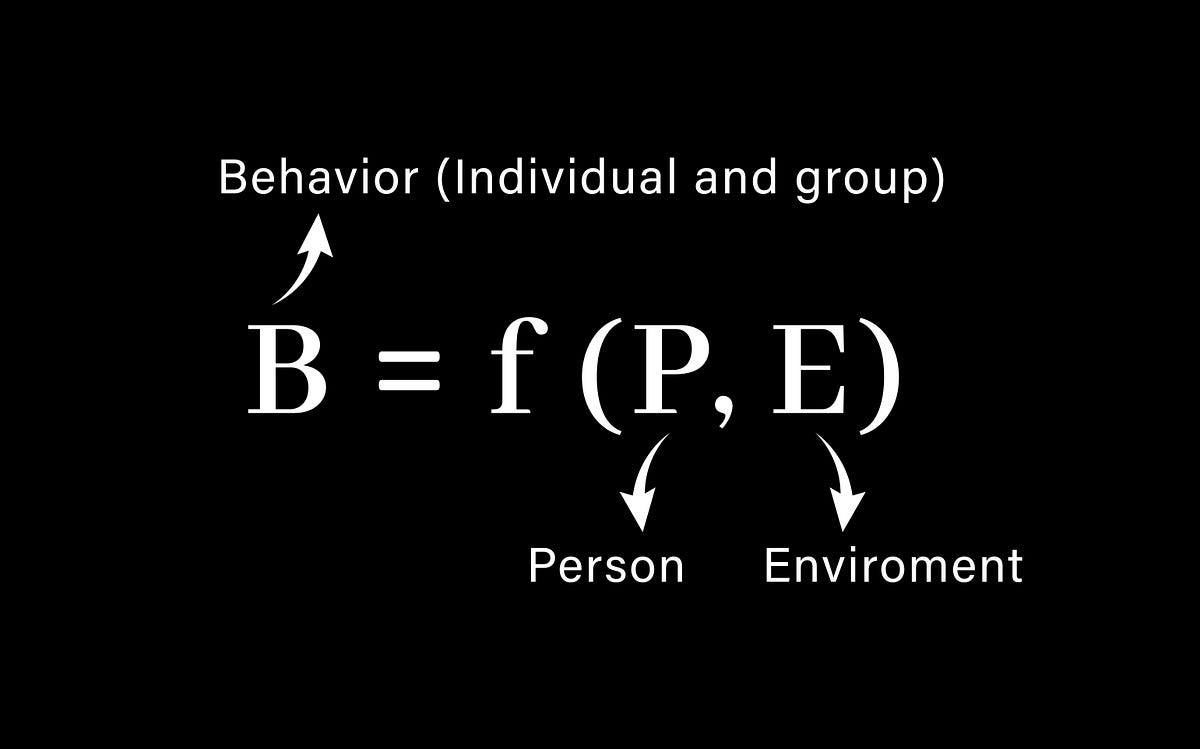
Human behaviour is a complex phenomenon influenced by a myriad of factors. However, renowned social psychologist Kurt Lewin introduced an equation that elegantly captures the essence of this intricate interplay. In this blog post, we delve into Lewin's equation, B=f(P,E), and explore how behaviour is shaped by the interaction between individuals and their environment.
Lewin's Equation
Kurt Lewin, a pioneer in the field of social psychology, provided us with this elegant equation: B=f(P,E). This equation represents the belief that human behaviour (B) is a function (f) of the person (P) and their environment (E). Let's break down each component to gain a deeper understanding of its significance.
The Person (P): The "P" in Lewin's equation refers to the individual, encompassing their unique characteristics, experiences, attitudes, and traits. Each person brings a distinct set of values, beliefs, and motivations that shape their behaviour. Factors such as personality, upbringing, genetics, and personal history all contribute to the person's disposition and influence how they respond to various situations. Much of our focus in trying to change behaviours are focussed in this area. Leadership development is based upon the Person being the centre of behaviour.
The Environment (E): The "E" in the equation represents the external factors and circumstances surrounding an individual. The environment encompasses physical, social, cultural, and situational elements that influence behaviour. For instance, social norms, family dynamics, educational institutions, work environments, and cultural values all play a role in shaping how individuals behave. I shall explore these areas in later blogs as this area is the least practiced in trying to align behaviour to organisational or societal goals.
The Interaction: Lewin's equation emphasizes that behaviour is not solely determined by either the person or the environment but is a result of their interaction. It recognises that individuals and their surroundings are in a constant state of reciprocal influence. People not only shape their environment but are also influenced by it. The way individuals interpret and respond to environmental cues is influenced by their internal predispositions, while the environment can provide opportunities or constraints that influence behaviour.
Implications and Applications: Lewin's equation has significant implications across various fields, including psychology, sociology, education, and management. By understanding the interaction between individuals and their environment, we can gain insights into predicting and influencing behaviour. When looking at aligning behaviours to new challenges, we should not assume behaviour is the consequence only of the person.
In organisational settings, managers can utilize Lewin's equation to design work environments that motivate and engage employees. By aligning the organisational culture, policies, and physical workspace with employees' needs and values, organisations can enhance productivity and job satisfaction.
Moreover, Lewin's equation reminds us of the importance of considering the broader context when analysing behaviour. It encourages us to move beyond individualistic explanations and recognise the role of external influences. This broader perspective can promote empathy, understanding, and more effective interventions in various personal and social contexts. These areas of Ecological Psychology I shall expand on in later blogs.
Kurt Lewin's equation, B=f(P,E), provides a powerful framework for understanding human behaviour. By acknowledging the dynamic interaction between individuals and their environment, we gain valuable insights into why people behave the way they do. Applying this equation in various domains allows us to create supportive environments, foster personal and professional growth, ultimately improve our understanding of why people behave in certain ways, and how we can encourage new behaviours to emerge.




Great blog Dave, I love how you clarify Lewin’s equation to show how it’s kept it’s relevance. Looking forward to reading about Ecological Psychology.
Thanks Dave. This blog is a great idea and I look forward to reading and engaging with it.